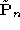 is the projection matrix which rectifies one of the two views, the
linear transformation (in projective coordinates) that maps the retinal
plane of
is the projection matrix which rectifies one of the two views, the
linear transformation (in projective coordinates) that maps the retinal
plane of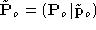 onto the rectified retinal plane is given by the matrix
onto the rectified retinal plane is given by the matrix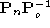 . For any 3-D point
w
we can write
. For any 3-D point
w
we can write
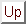

We now show that, if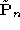 is the projection matrix which rectifies one of the two views, the
linear transformation (in projective coordinates) that maps the retinal
plane of
is the projection matrix which rectifies one of the two views, the
linear transformation (in projective coordinates) that maps the retinal
plane of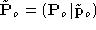 onto the rectified retinal plane is given by the matrix
onto the rectified retinal plane is given by the matrix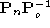 . For any 3-D point
w
we can write
. For any 3-D point
w
we can write
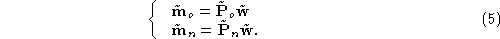
We know that the equation of the optical ray associated to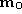 is
is
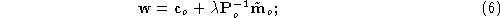
hence
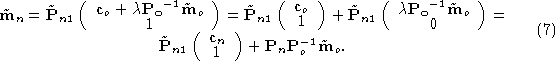
Assuming that rectification does not alter the optical center (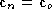 ), we obtain
), we obtain

This is a clearer and more compact result than the one reported in [
1
], in which is not written as the inverse of a projection matrix.
is not written as the inverse of a projection matrix.


Adrian F Clark