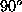 ,
,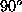 and
and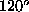 between the three surface normals, as well as the unit vector
constraints, The energy function is:
between the three surface normals, as well as the unit vector
constraints, The energy function is:


Figure
2
a (left) shows a tetrahedron with three faces visible, This object
involves three constraints represented by the three angles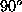 ,
,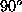 and
and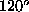 between the three surface normals, as well as the unit vector
constraints, The energy function is:
between the three surface normals, as well as the unit vector
constraints, The energy function is:
The data was acquired with a 3D triangulation range sensor. All
constraints were applied simultaneously according to algorithm
optim1
. The results are the average of 100 trials, with the initial vector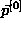 corrupted by a uniform deviation of scale
corrupted by a uniform deviation of scale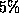 .
.
The angle constraint errors (Fig.
2
b) are decreasing linearly at a logarithmic scale. Both constraints are
highly satisfied for large value of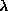 . One can observe that increasing
. One can observe that increasing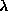 by factor of 10 leads nearly to an accuracy improvement factor of 10 in
the constraint. It is seen also that the least squares function
converges to a stable value, whereas the constraint function decreases
to zero at the end of the estimation (Fig.
2
c)
by factor of 10 leads nearly to an accuracy improvement factor of 10 in
the constraint. It is seen also that the least squares function
converges to a stable value, whereas the constraint function decreases
to zero at the end of the estimation (Fig.
2
c)
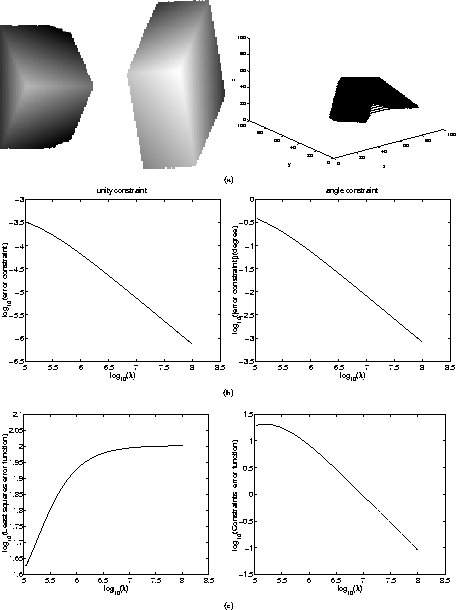
Figure:
(a) Acquired and segmented real data. (b) decrease of the unit vector
and the angle constraint error functions with respect to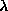 . (c) variation of the LS function and the constraint function with
respect to
. (c) variation of the LS function and the constraint function with
respect to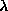 .
.
Naoufel Werghi