
Next:
Time-to-contact to curved surfaces
Up:
Affine Reconstruction of Curved
Previous:
Recovery of Curved surfaces
Up to now we have shown the affine reconstruction of curved surfaces. In
this section, we show that the affine reconstruction can be used for
distinguishing apparent contours from fixed features.
Substituting (
13
) into (
1
) and using (
8
) and (
12
), we find that the reconstructed contour generator,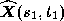 , at time
, at time can be projected back to a point,
can be projected back to a point,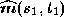 , in the original image at time
, in the original image at time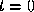 without any ambiguity. We now compute the differential component,
without any ambiguity. We now compute the differential component,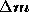 , between the projection,
, between the projection,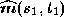 , and the contour curve,
, and the contour curve,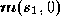 , in the image at time
, in the image at time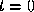 along the epipolar line. If the image curve is of a fixed feature, the
projection,
along the epipolar line. If the image curve is of a fixed feature, the
projection,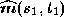 must coincide with
must coincide with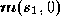 , and
, and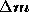 vanishes. If the image curve is an apparent contour,
vanishes. If the image curve is an apparent contour,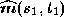 does not coincide with
does not coincide with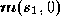 , and
, and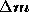 is not equal to zero. Thus, the magnitude
is not equal to zero. Thus, the magnitude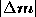 is a good measure for distinguishing apparent contours from fixed
features. Even if the camera is uncalibrated, we can distinguish
apparent contours from fixed features by using the projection of
reconstructed contour generators back into the images.
is a good measure for distinguishing apparent contours from fixed
features. Even if the camera is uncalibrated, we can distinguish
apparent contours from fixed features by using the projection of
reconstructed contour generators back into the images.
J. Sato
Mon Jul 7 22:39:50 BST 1997
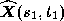 , at time
, at time can be projected back to a point,
can be projected back to a point,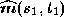 , in the original image at time
, in the original image at time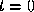 without any ambiguity. We now compute the differential component,
without any ambiguity. We now compute the differential component,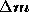 , between the projection,
, between the projection,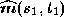 , and the contour curve,
, and the contour curve,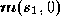 , in the image at time
, in the image at time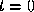 along the epipolar line. If the image curve is of a fixed feature, the
projection,
along the epipolar line. If the image curve is of a fixed feature, the
projection,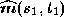 must coincide with
must coincide with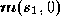 , and
, and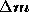 vanishes. If the image curve is an apparent contour,
vanishes. If the image curve is an apparent contour,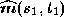 does not coincide with
does not coincide with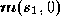 , and
, and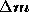 is not equal to zero. Thus, the magnitude
is not equal to zero. Thus, the magnitude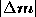 is a good measure for distinguishing apparent contours from fixed
features. Even if the camera is uncalibrated, we can distinguish
apparent contours from fixed features by using the projection of
reconstructed contour generators back into the images.
is a good measure for distinguishing apparent contours from fixed
features. Even if the camera is uncalibrated, we can distinguish
apparent contours from fixed features by using the projection of
reconstructed contour generators back into the images.